Introduction
In a solar rooftop system, the solar panels are installed in the roof of any residential, commercial, institutional and industrial buildings. This can be of two types (i) Solar Rooftop System with storage facility using battery, and (ii) Grid Connected Solar Rooftop System.
(i) Solar Rooftop System with storage facility using battery: Such rooftop system has battery as storage facility. The solar electricity is stored in the battery and can be utilized during night also when the sun is not available.
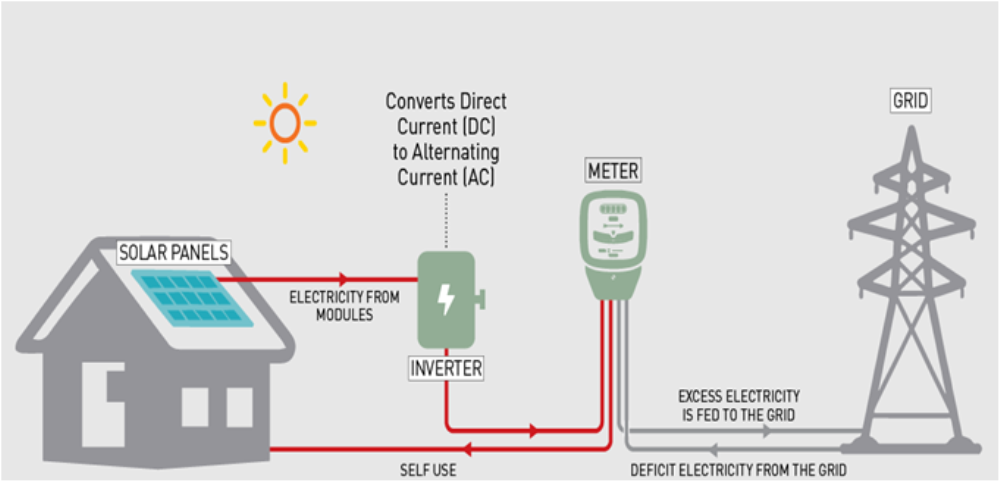
(ii) Grid Connected Solar Rooftop System: These systems generate power during the day time which is utilized fully by powering captive loads and feed excess power to the grid as long as grid is available. In case, where solar power is not sufficient due to cloud cover etc., the captive loads are served by drawing power from the grid.
How does solar rooftop system work?
Basically government is motivating for the upliftment of Grid Connected Solar Rooftop System by providing different subsidy schemes.